What is CT Scanning of the Body?
CT scanning—sometimes called CAT scanning—is a noninvasive medical test that helps physicians diagnose and treat medical conditions.
CT scanning combines special x-ray equipment with sophisticated computers to produce multiple images or pictures of the inside of the body. These cross-sectional images of the area being studied can then be examined on a computer monitor or printed.
CT scans of internal organs, bone, soft tissue and blood vessels provide greater clarity and reveal more details than regular x-ray exams.
Using specialized equipment and expertise to create and interpret CT scans of the body, radiologists can more easily diagnose problems such as cancers, cardiovascular disease, infectious disease, trauma and musculoskeletal disorders.
What are some common uses of the procedure?
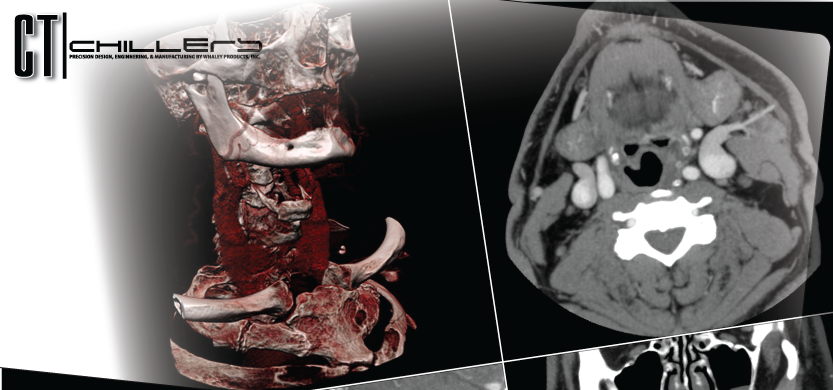
CT of the lungs, window level set to demonstrate the vessels and air ways – not intended to demonstrate the heart, spine muscles etc. This is used to look for things like pneumonia or lung cancer.
CT imaging is:
one of the best and fastest tools for studying the chest, abdomen and pelvis because it provides detailed, cross-sectional views of all types of tissue.
often the preferred method for diagnosing many different cancers, including lung, liver and pancreatic cancer, since the image allows a physician to confirm the presence of a tumor and measure its size, precise location and the extent of the tumor’s involvement with other nearby tissue.
an examination that plays a significant role in the detection, diagnosis and treatment of vascular diseases that can lead to stroke, kidney failure or even death. CT is commonly used to assess for pulmonary embolism (a blood clot in the lung vessels) as well as for abdominal aortic aneurysms (AAA).
invaluable in diagnosing and treating spinal problems and injuries to the hands, feet and other skeletal structures because it can clearly show even very small bones as well as surrounding tissues such as muscle and blood vessels.
Physicians often use the CT examination to:
quickly identify injuries to the lungs, heart and vessels, liver, spleen, kidneys, bowel or other internal organs in cases of trauma.
guide biopsies and other procedures such as abscess drainages and minimally invasive tumor treatments.
plan for and assess the results of surgery, such as organ transplants or gastric bypass.
stage, plan and properly administer radiation treatments for tumors as well as monitor response to chemotherapy.
measure bone mineral density for the detection of osteoporosis.
 Packaged Chillers Non-expandable (integrated pump tank) 1.5Ton – 20Ton Single / Dual Circuits Single / Dual Pumps |
 SAE Series Modular Chillers Expandable (pump & tank on separate skid) 1.5Ton – 200Ton Single / Dual Circuits |
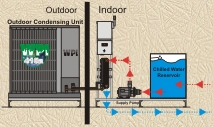 SAR Series Split Chillers Expandable (Outdoor Condensing Unit) (pump, tank, evaporator on indoor skid) 1.5Ton – 200Ton Single / Dual Circuits |
